Jan . 15, 2024 16:05 Back to list
distributed energy management system
Renewable energy

Renewable energyisenergyfromrenewable resourcesthat are naturally replenished on ahuman timescale. Renewable resources includesunlight,wind, themovement of water, andgeothermal heat.[2][3]Although most renewable energy sources aresustainable, some are not. For example, somebiomasssources are considered unsustainable at current rates ofexploitation.[4][5]Renewable energy is often used forelectricity generation,heating and cooling. Renewable energy projects are typically large-scale, but they are also suited toruraland remote areas anddeveloping countries, where energy is often crucial inhuman development.[6][7]
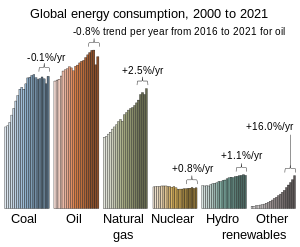
Renewable energy is often deployed together with furtherelectrification, which has several benefits: electricity canmove heator objects efficiently, and is clean at the point of consumption.[8][9]From 2011 to 2021, renewable energy grew from 20% to 28% of global electricity supply. Use offossil energyshrank from 68% to 62%, and nuclear from 12% to 10%. The share of hydropower decreased from 16% to 15% while power from sun and wind increased from 2% to 10%.Biomassand geothermal energy grew from 2% to 3%. There are 3,146 gigawatts installed in 135 countries, while 156 countries have laws regulating the renewable energy sector.[10][11]In 2021, China accounted for almost half of the global increase in renewable electricity.[12]
Globally there are over 10 million jobs associated with the renewable energy industries, withsolar photovoltaicsbeing the largest renewable employer.[13]Renewable energy systems are rapidly becoming more efficient and cheaper and their share of total energy consumption is increasing,[14]with a large majority of worldwide newly installed electricity capacity being renewable.[15]In most countries,photovoltaic solaroronshore windare the cheapest new-build electricity.[16]
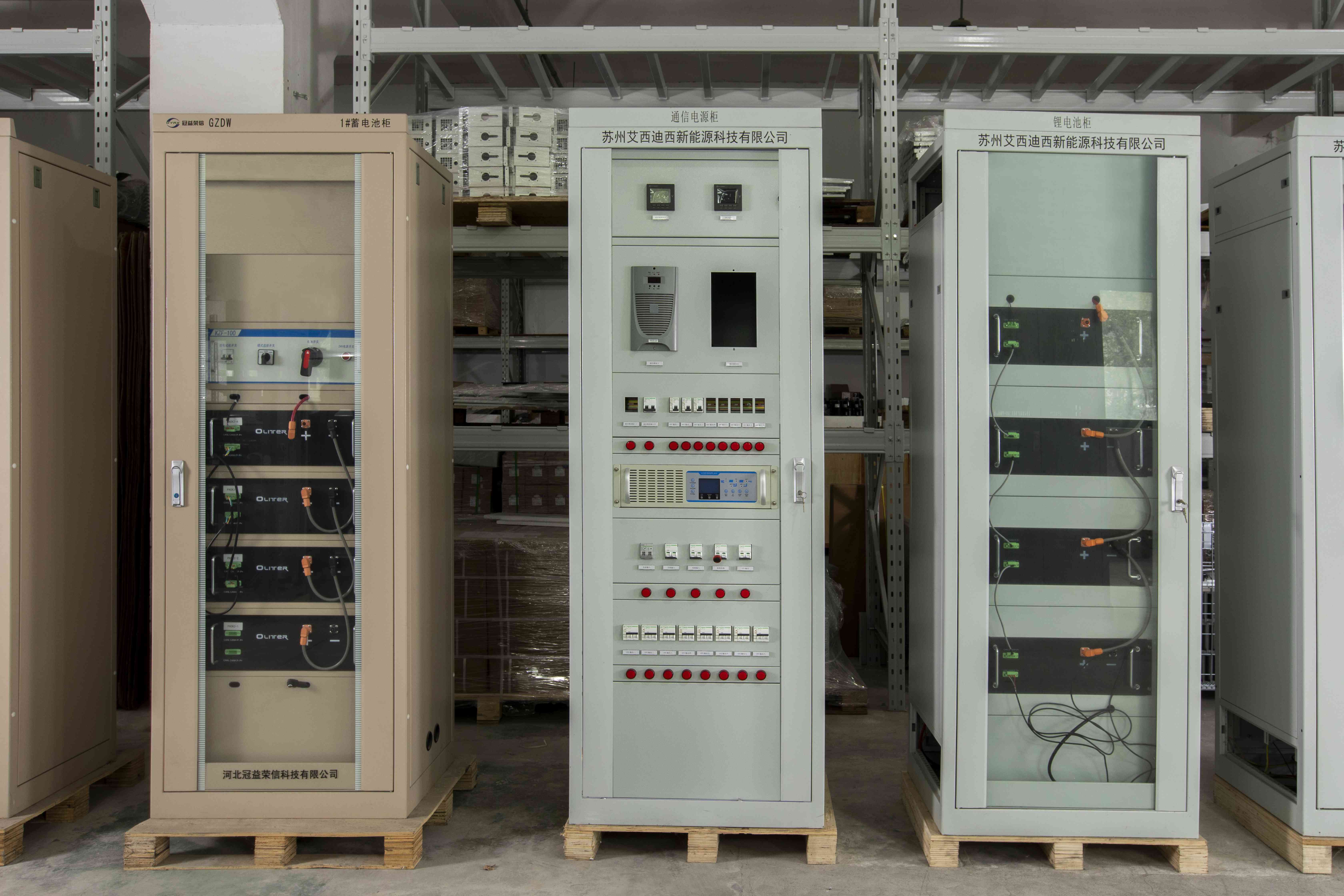
Grid level protection Self-Cooling Outdoor Distributed Energy Storage Cabinet - Power Type PW-164
Many nations around the world already have renewable energy contributing more than 20% of their total energy supply, withsome generating over half their electricity from renewables.[17]A few countries generate all their electricity using renewable energy.[18]National renewable energy markets are projected to continue to grow strongly in the 2020s and beyond.[19]According to the IEA, to achieve net zero emissions by 2050, 90% of global electricity generation will need to be produced from renewable sources.[20]Some studies have shown that a global transition to100% renewable energyacross all sectors – power, heat, transport and industry – is feasible and economically viable.[21][22][23]
Renewable energy resources exist over wide geographical areas, in contrast tofossil fuels, which are concentrated in a limited number of countries. Deployment of renewable energy andenergy efficiencytechnologies is resulting in significantenergy security,climate change mitigation, and economic benefits.[24]However renewables are being hindered by hundreds of billions of dollars offossil fuel subsidies.[25]In internationalpublic opinion surveysthere is strong support for renewables such as solar power and wind power.[26][27]In 2022 theInternational Energy Agencyasked countries to solve policy, regulatory, permitting and financing obstacles to adding more renewables, to have a better chance of reachingnet zero carbon emissionsby 2050.
Overview[edit]
Definition
Renewable energy flows involve natural phenomena such assunlight,wind,tides,plant growth, andgeothermal heat, as theInternational Energy Agencyexplains:[30]
Renewable energy is derived from natural processes that are replenished constantly. In its various forms, it derives directly from the sun, or from heat generated deep within the earth. Included in the definition is electricity and heat generated from solar, wind, ocean,hydropower, biomass, geothermal resources, and biofuels and hydrogen derived from renewable resources.
Drivers and benefits[edit]
Renewable energy stands in contrast tofossil fuels, which are being used far more quickly than they are being replenished. Renewable energy resources and significant opportunities forenergy efficiencyexist over wide geographical areas, in contrast to other energy sources, which are concentrated in a limited number of countries. Rapid deployment of renewable energy and energy efficiency, and technological diversification of energy sources, would result in significantenergy securityand economic benefits.[24]Solar and wind power have got much cheaper.[31]In some cases it will be cheaper to transition to these sources as opposed to continuing to use the current, inefficient, fossil fuels. In addition, electrification with renewable energy is more efficient and therefore leads to significant reductions in primary energy requirements.[32][clarification needed]It would also reduce environmentalpollutionsuch asair pollutioncaused by the burning of fossil fuels, and improve public health, reduce premature mortalities due to pollution and save associated health costs that could amount to trillions of dollars annually.[33][34]Multiple analyses of decarbonization strategies have found thatquantified health benefitscan significantly offset the costs of implementing these strategies.[35][36]
Climate changeconcerns, coupled with the continuing fall in the costs of some renewable energy equipment, such as wind turbines and solar panels, are driving increased use of renewables.[26]New government spending, regulation and policies helped the industry weather theglobal financial crisisbetter than many other sectors.[37]As of 2019, however, according to theInternational Renewable Energy Agency, renewables overall share in the energy mix (including power, heat and transport) needs to grow six times faster, in order to keep the rise in average global temperatures "well below" 2.0 °C (3.6 °F) during the present century, compared to pre-industrial levels.[38]
Scale[edit]
A household's solar panels, and batteries if they have them, can often either be used for just that household or if connected to an electrical grid can be aggregated with millions of others.[39]Over 44 million households usebiogasmade in household-scale digesters forlightingand/orcooking, and more than 166 million households rely on a new generation of more-efficient biomass cookstoves.[40][needs update]
According to the research, a nation must reach a certain point in its growth before it can take use of more renewable energy. In our words, its addition changed how crucial input factors (labor and capital) connect to one another, lowering their overallelasticityand increasing the apparent economies of scale.[41]United Nations' eighth Secretary-GeneralBan Ki-moonhas said that renewable energy has the ability to lift the poorest nations to new levels of prosperity.[42]At the national level, at least 30 nations around the world already have renewable energy contributing more than 20% of energy supply.[43]Although many countries have various policy targets for longer-term shares of renewable energy these tend to be only for the power sector,[44]including a 40% target of all electricity generated for the European Union by 2030.[45]
Uses[edit]
Renewable energy often displaces conventional fuels in four areas:electricity generation,hot water/space heating,transportation, and rural (off-grid) energy services.[46]
More than a quarter of electricity is generated from renewables as of 2021.[47]One of the efforts to decarbonize transportation is the increased use ofelectric vehicles(EVs).[48]Despite that and the use ofbiofuels, such asbiojet, less than 4% of transport energy is from renewables.[49]Occasionallyhydrogen fuel cellsare used for heavy transport.[50]Meanwhile, in the futureelectrofuelsmay also play a greater role in decarbonizing hard-to-abate sectors like aviation and maritime shipping.[51]
Solar water heatingmakes an important contribution torenewable heatin many countries, most notably in China, which now has 70% of the global total (180 GWth). Most of these systems are installed on multi-family apartment buildings[52]and meet a portion of the hot water needs of an estimated 50–60 million households in China. Worldwide, total installed solar water heating systems meet a portion of the water heating needs of over 70 million households.
Heat pumpsprovide both heating and cooling, and also flatten the electric demand curve and are thus an increasing priority.[53]Renewable thermal energyis also growing rapidly.[54]About 10% of heating and cooling energy is from renewables.[47]
-
Advanced AI Energy Management with GPT-4 Turbo
NewsAug.02,2025
-
AI-Powered EMS with GPT-4-Turbo | Efficiency Boost
NewsAug.01,2025
-
Optimized Storage System for GPT-4-Turbo | High Performance
NewsJul.31,2025
-
AI Energy Management System w/ GPT-4 Turbo Efficiency
NewsJul.31,2025
-
High-Performance Energy Storage System for Reliable Power Solutions
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Advanced EMS Solutions for Energy Management System & Storage Battery Companies
NewsJul.29,2025
























